
(Wikipedia)
Oxacillin (Handelsname: InfectoStaph® (D), Stapenor® Salbe ad us.vet. (Rinder) (D)[4]) ist ein Antibiotikum der Klasse der Isoxazolylpenicilline; sogenannte Staphylokokken-Penicilline.
Klinischer Wirkungsbereich von Oxacillin sind penicillinasebildende Staphylokokken-Staemme. Es wird heute als eines der Leitantibiotika fuer die bedeutsamen nosokomialen Infektionen mit multiresistenten Staphylococcus aureus-Staemmen verwendet, man spricht in diesem Falle von Oxacillin-Resistenten-Staphylococcus-aureus-Staemmen, kurz ORSA. Gleichbedeutend ist die historische, haeufiger verwendete Bezeichnung als Methicillin-resistenter Staphylococcus aureus, kurz MRSA.
Weitere penicillinaseresistente Antibiotika sind Cloxacillin, Dicloxacillin, Flucloxacillin und Methicillin, wobei Methicillin heutzutage weder therapeutisch noch fuer die Testung der Empfindlichkeit eingesetzt wird. (Wikipedia)
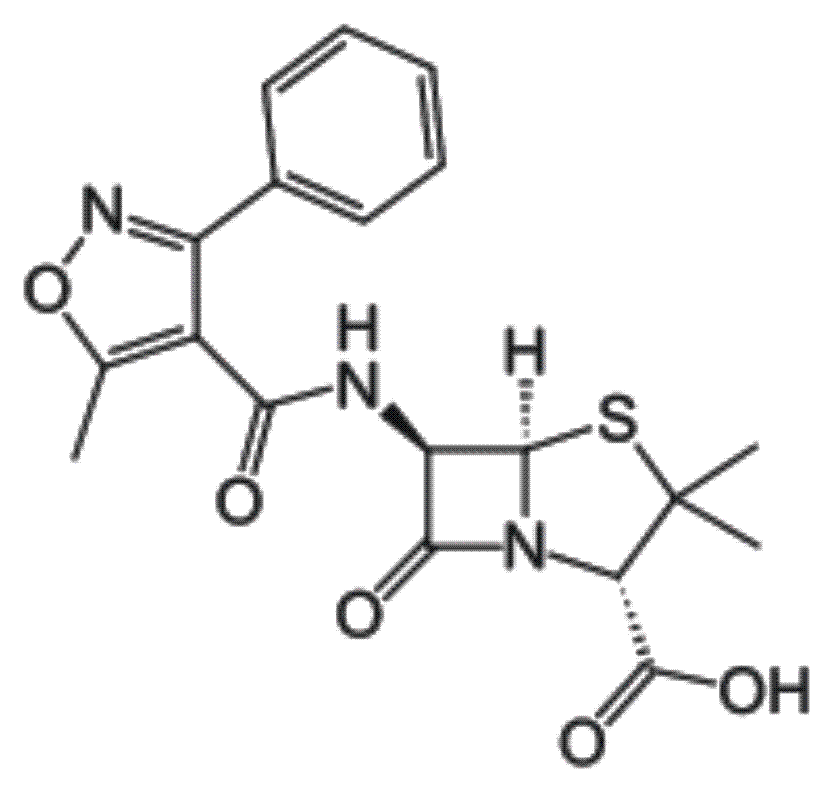
(2S,5R,6R)-3,3-Dimethyl-6- (5-methyl-3-phenyl- isoxazol-4-ylcarboxamido)-7-oxo-4-thia-1- azabicyclo[3.2.0]-heptan-2-carbonsaeure (IUPAC); (Wikipedia)
Oxacillin-Freebase:
Summenformel: C19H19N3O5S (Oxacillin);
Molare Masse: 401,44 g/mol-1;
pKs-Wert: 2,72;
Wasserloeslichkeit: 27,8 mg/l-1 bei 25 Grad Celsius; (Wikipedia)
Mononatriumsalz-Monohydrat von Oxacillin:
C19H18N3NaO5S/H2O (Mononatriumsalz-Monohydrat);
Schmelzpunkt: 188 Grad Celsius (Oxacillin-Mononatriumsalz-Monohydrat);(Wikipedia)
LD50: 1490 mg/kg-1 (Maus i.v.); (Wikipedia)
Die Verbindung wirkt antibiotisch. (Wikipedia)